Visceral Ischemia
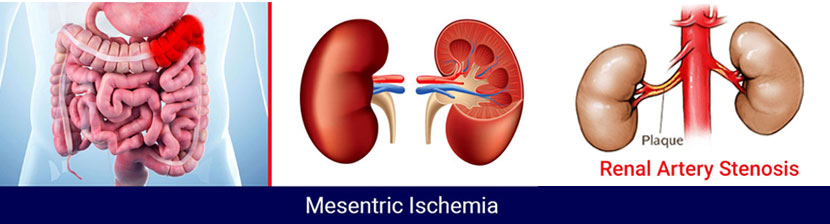
Visceral ischemia refers to a condition where the blood flow to the intestines or abdominal organs is reduced or blocked, usually due to narrowing or blockage in the mesenteric arteries. This can be acute (sudden onset, often a medical emergency) or chronic (gradually developing over time). The most common causes include atherosclerosis, blood clots, or arterial dissection. Reduced blood supply leads to oxygen deprivation in the intestines, which, if untreated, can cause severe pain, tissue damage, and even life-threatening complications.
Patients with chronic visceral ischemia often experience post-meal abdominal pain, unintentional weight loss, and fear of eating due to discomfort. Acute cases may present with sudden, severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and signs of shock. Early diagnosis and treatment by a skilled Vascular & Endovascular Surgeon are crucial for preventing irreversible damage.
Symptoms
- Acute mesenteric ischemia
Signs and symptoms of the acute form of mesenteric ischemia include: - Abrupt, severe abdominal pain
- Urgent need to have a bowel movement
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Chronic mesenteric ischemia
Signs and symptoms of the chronic form of mesenteric ischemia include: - Abdominal pain that starts about 30 minutes after eating
- Pain that worsens over an hour
- Pain that goes away within one to three hours
Treatment Types
1. Medical ManagementBook Your Consultation Today
Say goodbye to leg pain and unsightly veins. Schedule a vascular consultation with Dr. Ritesh Gaikwad today.
- Clinics: Thane ( Ghodbunder road, Hiranandani estate, Kasarwadavali) and Mumbai
- Website: www.drriteshgaikwad.com
- Phone: +91-9619332942 / 9620962942
- Email: drriteshgaikwad19@gmail.com